The budget should reflect the full scope of activities with sufficient detail so that a reviewer can assess 1) whether all relevant components and activities were included and 2) the appropriateness of the budget for each component.
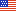
The general model for the life cycle of a clinical trial is based on the following paradigm.
General Clinical Trial Process Outline
Proposed clinical trial budgets must account for all necessary activities and contain enough specificity in each line item to allow for appropriate review. A comprehensive budget proposal might include the following:
- Protocol design and development costs
- Subject matter expert consultation
- Background preparation
- Protocol document preparation
- Sample size calculation
- Determination of sample size considerations, including
- Method for estimating sample size based on either
- Estimated effect size from prior data or
- Need to determine effect size in the target population
- Multi-arm study
- Minimal difference in effect size to be of clinical interest or significance
- Justification for minimal difference in effect size
- Method for estimating sample size based on either
- Attrition, drop outs, and non-compliance accounted for?
- Estimates and factors used to determine
- Number of informative events to analyze
- Per participant
- Total based on number of participants and number of visits per participant
- Determination of sample size considerations, including
- Agreements and other legal documents: preparation and execution
- Approvals
- Oversight
- External monitoring
- Protocol training for study team
- Data capture and storage
- Database preparation
- Data security procedures
- Logistics for each visit or encounter regarding personnel, location, supplies, processing, storage, transport, tracking
- Location
- Frequency
- Equipment
- Intervention procurement and preparation
- Experimental
- Standard therapy or intervention for the disease or condition under study
- Procedures for administration
- Experimental
- Standard therapeutic
- Assessments
- Experimental
- Standard therapeutic
- Processing of collected data and specimens
- Data and specimen preparation
- Storage
- Packaging and shipping
- Additional data capture
- From medical and administrative records
- From study-specific instruments that require further processing
- From recordings (video, auditory, still images)
- Analysis
- Personnel
- Preparation of analytic data sets
- Methods
- Data dissemination
- Presentations
- Publications
- Data sharing
- Submit to pre-existing data enclave with governance structure
- Establish independent data enclave and governance