Michael Hoa, M.D., Principal Investigator
Research Statement
The Auditory Development and Restoration Program, part of the Section on Inner Ear Therapeutics within NIDCD’s Neurotology Branch, investigates the development and function of adult cochlear cell types and their relationship to disorders of hearing instability (HI). The long-term goal of the lab is to identify therapeutic targets and novel treatments for HI disorders, including Ménière’s disease, autoimmune inner ear disease, sudden sensorineural hearing loss, and enlarged vestibular aqueduct syndrome. We ultimately seek to identify ways to enable hearing restoration in the adult inner ear.
Human diseases with HI and progressive hearing loss have few, if any, effective treatments. Included in HI disorder presentations are patients who experience sudden changes in hearing (e.g., sudden sensorineural hearing loss) as well as patients who experience hearing fluctuation (e.g., autoimmune inner ear disease, Ménière’s disease, and enlarged vestibular aqueduct syndrome). There is an unmet need to identify and define underlying mechanisms, as well as common and distinct phenotypic and etiologic factors contributing to HI disorders. Previous work in this lab has defined the transcriptional landscape of stria vascularis and surrounding cell types in the adult mouse cochlea. The stria vascularis is housed in the lateral wall of the cochlea and is essential for regulating ion homeostasis and generating the endocochlear potential (EP), which is essential for proper hair cell function and hearing.
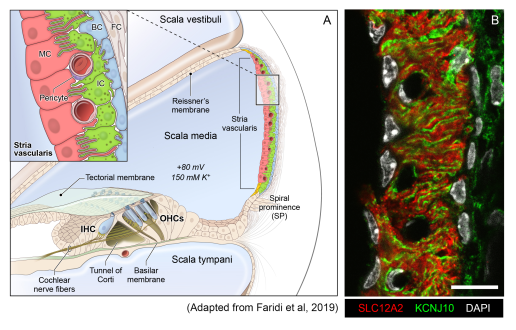
Stria vascularis cellular heterogeneity and organization
(A): Schematic of the stria vascularis (SV) and its relationship to structures in the cochlea. The SV is composed of three layers of cells and is responsible for generating the +80 mV endocochlear potential (EP) and the high potassium concentration in the endolymph-containing scala media. The relationship between the marginal, intermediate, and basal cells are demonstrated with the marginal extending basolateral projections to interdigitate with intermediate cells, which have bidirectional cellular projections that interdigitate with both marginal and basal cells. In addition to these cell types, other cell types, including spindle cells (yellow), endothelial cells, pericytes, and macrophages (not shown) are present in the SV.
(B): Cross-section of the SV in a postnatal day 30 (P30) mouse immunostained with anti-SLC12A2 (marginal cells, red), anti-KCNJ10 (intermediate cells, green), and DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) for nuclei. Notice the interdigitation of cellular processes from both intermediate and marginal cells. Scale bar is 20 μm.
Source: Korrapati S, Taukulis I, Olszewski R, Pyle M, Gu S, Singh R, Griffiths C, Martin D, Boger E, Morell J, Hoa M. Single cell and single cell nucleus RNA-Seq reveal cellular heterogeneity and homeostatic regulatory networks in adult mouse stria vascularis. Front Mol Neurosci 2019 Dec 20.
doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00316. eCollection 2019.
Human temporal bone studies demonstrate endolymphatic hydrops—an expansion of the endolymph-containing scala media of the cochlea—in some patients with HI disorders. This suggests an underlying issue related to cochlear ionic homeostasis, but the underlying mechanisms remain poorly characterized. More generally, our understanding of cochlear health—defined as the anatomical and functional status of the diverse cochlear cell types and tissues as well as other biological factors that enable or are important for hearing—remains limited. A lack of understanding of these pathogenic mechanisms has hindered the discovery of effective therapeutics to reverse or even stabilize the disease process of HI disorders.
The overall goals of the lab are to:
- Identify novel and repurposable treatments along with druggable gene targets in the setting of hearing fluctuation and inflammation and to utilize these treatments to gain insight into the mechanisms underlying HI.
- Establish a multi-omic cellular basis for human cochlear health and better define the transcriptional underpinnings of HI disorders, including (most commonly) Ménière’s disease.
- Perform deep phenotyping of patients with HI disorders to define biomarkers (radiologic, audiometric, immunologic, and multi-omic) that correlate with presence and changes in endolymphatic hydrops and changes in hearing.
Current projects in the lab fall under these three main aims and are highly collaborative. Work at the bench involves both investigations in mouse models and human tissues, including archival human temporal bone tissue and human samples obtained from patients with HI disorders. Work in the clinical and bioinformatic realm includes a deep phenotyping clinical protocol that seeks to identify diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic molecular and electrophysiologic biomarkers (audiometric, radiologic, and hematologic/immunologic) that correlate with presence and changes in endolymphatic hydrops and changes in hearing. The clinical protocol seeks to establish a basis for identifying novel and repurposable treatments for patients with HI disorders.
Techniques employed by the lab include immunohistochemistry, confocal laser microscopy, animal auditory function testing, molecular biology techniques, multi-omic approaches (i.e., single-cell, single-nucleus, and spatial transcriptome, proteome, cytokinome), flow cytometry, bioinformatic methods (machine- and deep-learning-based approaches, computer vision, biostatistical modeling), and clinic-based investigation. Developing work in the lab involves clinical investigation of biomarkers of cochlear health. The lab is adaptive and seeks to use techniques that help address the fundamental aims of the lab.
In addition to the above, the lab has a strong interest in fostering the next generation of clinician-scientists and translational scientists who will seek to advance the care of human hearing loss.
Collaborators
- NIDCD Audiology Unit (Principal Investigator: Gayla Poling, Ph.D.)
- NINDS Proteomics Core Facility (Director: Yan Li, Ph.D.)
- NIDCR Combined Technical Research Core (Director: Mehrnoosh Abshari, M.S.)
- NIDCD Genomics and Computational Biology Core (Director: Robert J. Morell, Ph.D.)
- NINDS Quantitative MRI (qMRI) Core Facility (Co-Director: Govind Bhagavastheeshwaran, Ph.D.)
- NIDCD Data Science Core (Director: Hui Cheng, Ph.D.)
- NIAMS Translational Immunology Section (Director: Massimo Gadina, Ph.D.)

Lab staff as of 2025 (L-R): Julia Telischi, Samuel Adadey, Rafal T. Olszewski, Shoujun Gu, Michael Hoa.