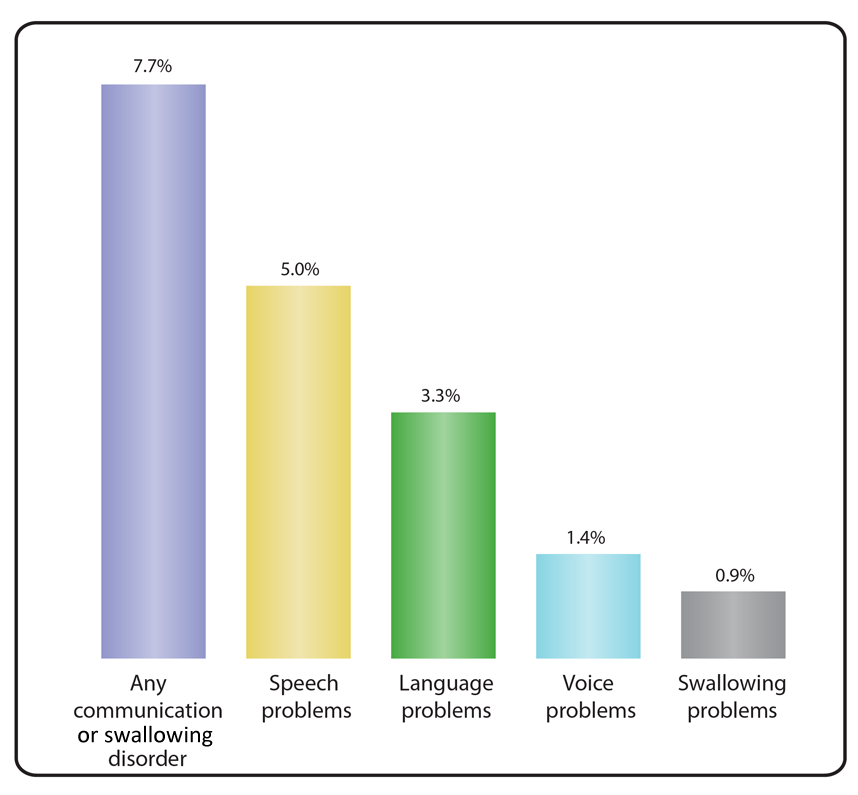
In 2012, 7.7% of children ages 3–17 years had a communication or swallowing disorder during the past 12 months. Speech problems were the most prevalent type of communication disorder (5.0%), while swallowing problems were the least prevalent (0.9%). Language problems (3.3%) and voice problems (1.4%) were also prevalent.
Notes
Data are based on household interviews with parents or adult caregivers of children in a sample of the civilian noninstitutionalized U.S. population. Children could have more than one type of communication or swallowing disorder.
Data source
CDC/NCHS, National Health Interview Survey, 2012
Definitions
Speech problem: Based on a positive response to the question, "During the past 12 months, has [sample child] had a problem speaking, such as making speech sounds correctly or stuttering, that lasted for a week or longer?"
Language problem: Based on a positive response to the question, "During the past 12 months, has [sample child] had a problem learning, using, or understanding words or sentences that lasted for a week or longer?"
Voice problem: Based on a positive response to the question, “During the past 12 months, has [sample child] had any problems or difficulties with his/her voice, such as too weak, hoarse, or strained, that lasted for a week or longer?"
Swallowing problem: Based on a positive response to the question, "During the past 12 months, has [sample child] had a problem swallowing food or beverages that lasted for a week or longer?"
Communication disorder: Based on a positive response to at least one of the four problems listed above. Disorders were parent-reported and not necessarily diagnosed by a doctor or health care professional.
Receipt of intervention services: Respondents who indicated that the sample child had a speech, language, voice, or swallowing problem were then asked the following question separately for each type of communication disorder, "During the past 12 months, did [sample child] receive speech language therapy or other intervention services for his/her 1) voice problems; 2) problems swallowing, 3) speech problems; 4) using, learning, or understanding words or sentences; respectively?"